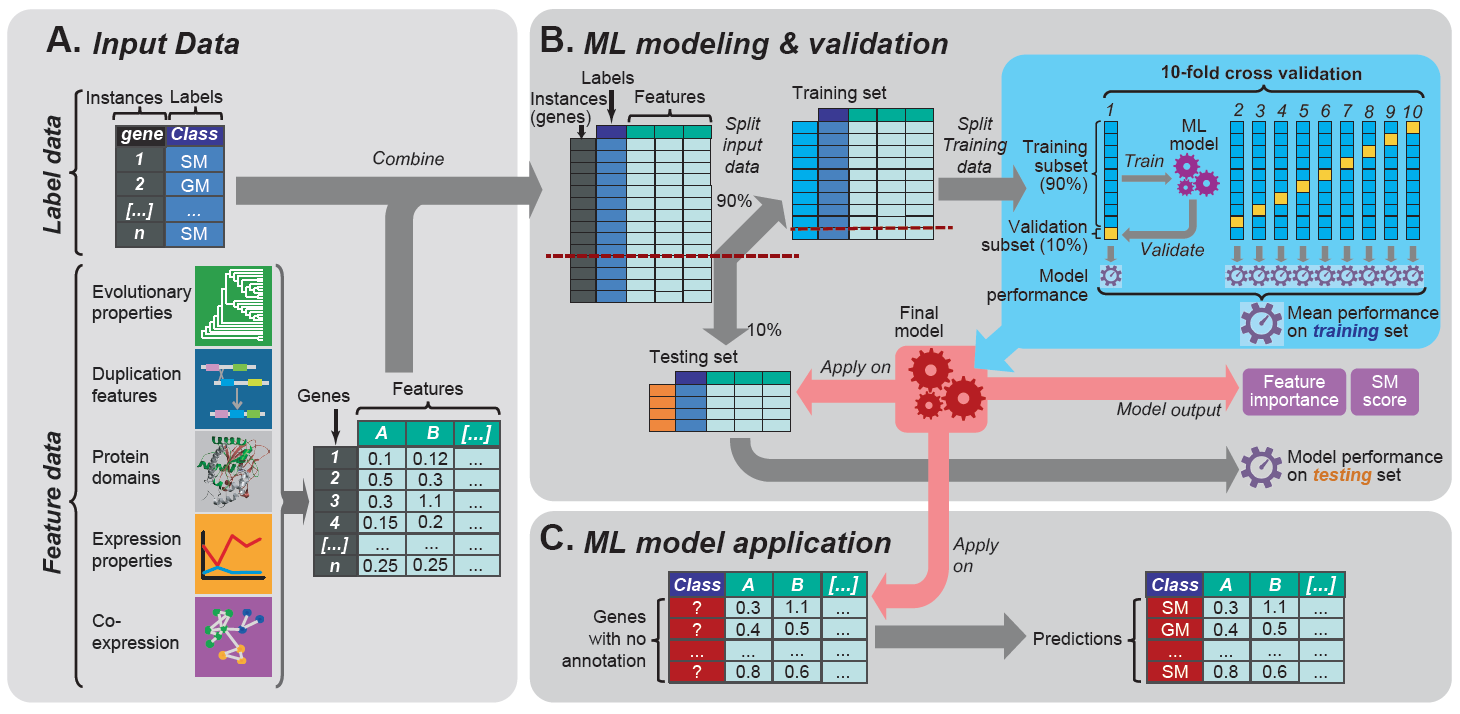
With the increase of sequenced non-model species, a major challenge in plant biology is to ascertain gene function. Genes involved in specialized metabolism (SM), or metabolism specific to a certain plant lineage, are not well known because of the sizeable diversity of specialized metabolites (SMs) among plant species. Additionally, model species such as Arabidopsis thaliana have large amounts of experimentally-backed annotations that non-model species lack. We have built machine learning models which can both predict SM genes within the model species A. thaliana and use information from A. thaliana to predict SM genes in tomato, a less well annotated species with interesting specialized metabolites.